Top Stories of 2023: Climate Change Research, Space Discoveries and More
2023 has been a year full of discovery for the College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences (CMNS). CMNS students, faculty and staff members revealed new information about our changing climate, identified potential signs of life in space and reported their knowledge of large language models like ChatGPT.
As 2023 comes to a close, take some time to revisit our most-read stories of the year and discover some that you may have missed.
- New Study Confirms Presence of Flesh-Eating and Illness-Causing Bacteria in Florida’s Coastal Waters Following Hurricane Ian – When Hurricane Ian struck southwest Florida in September 2022, it unleashed a variety of Vibrio bacteria that can cause illness and death in humans, according to an October 2023 study led by Rita Colwell, a Distinguished University Professor in the University of Maryland Institute for Advanced Computer Studies who has studied Vibrio for the last 50 years. With warming oceans expected to fuel wetter and more powerful storms like Ian, coastal communities could see more Vibrio infections in the future.
- UMD Researchers Identify Protein that Counteracts Key Rattlesnake Venom Toxins – To reduce and mitigate the severity of venomous snake bites, a team of University of Maryland biologists led by Biology Distinguished University Professor Sean Carroll launched an investigation into the genome of the western diamondback rattlesnake. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team’s findings have notable implications for the development of improved snake bite treatments.
- Is AI-Generated Content Actually Detectable? – UMD artificial intelligence experts Soheil Feizi and Furong Huang shared their latest research on large language models like ChatGPT.
- Where Did Earth’s Water Come From? Not Melted Meteorites, According to Scientists – A March 2023 study published in Nature brought scientists one step closer to answering where Earth’s water originated. Led by Geology Assistant Professor Megan Newcombe, researchers analyzed 4.5 billion-year-old melted meteorites and found they had extremely low water content—in fact, they were among the driest extraterrestrial materials ever measured.
- Humans Are Disrupting Natural ‘Salt Cycle’ on a Global Scale, New Study Shows – The planet’s demand for salt comes at a cost to the environment and human health, according to an October 2023 scientific review led by Geology Professor Sujay Kaushal. The paper revealed that human activities are making Earth’s air, soil and freshwater saltier, which could pose an “existential threat” if current trends continue.
- University of Maryland Senior Kevin Tu Named 2023 Churchill Scholar – Kevin Tu (B.S. ‘23 biological sciences; B.S. ‘23, economics) was awarded full funding to pursue a one-year master’s degree at the University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom. Tu is now pursuing a Master of Philosophy degree in oncology, with a research focus on using machine learning to develop a cost-effective clinical test that will subtype breast cancers based on genetic information and identify each tumor’s specific driver mutations.
- Joshua Weitz Joins UMD’s Department of Biology as the Clark Leadership Chair in Data Analytics – An award-winning author who has published more than 140 peer-reviewed journal papers, Joshua Weitz joined the Biology Department in July 2023. Weitz studies how viruses transform human health and the fate of our planet.
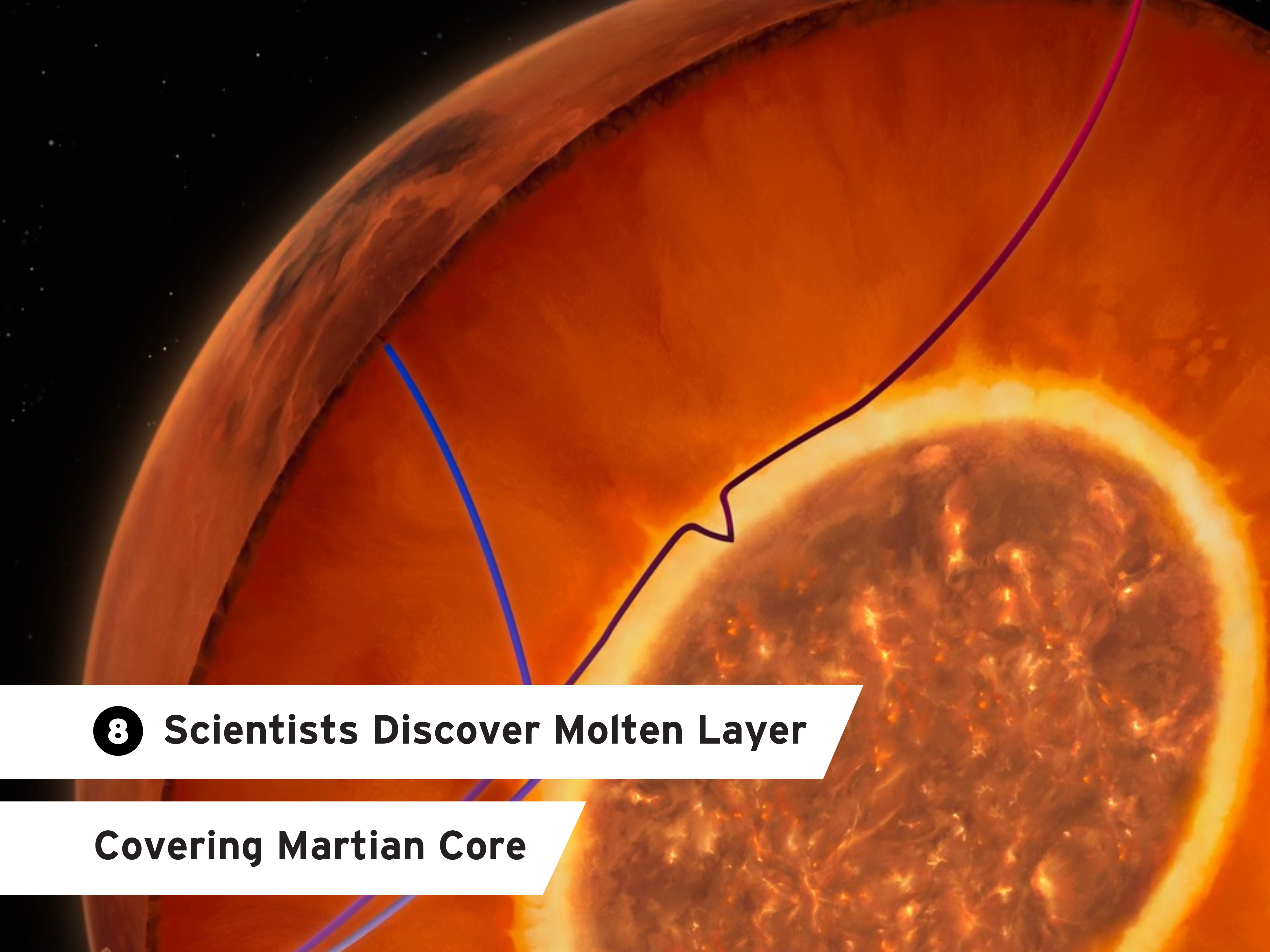
- Scientists Discover Molten Layer Covering Martian Core – NASA InSight research co-authored by Geology Professor Vedran Lekic in Nature revealed a liquid silicate ‘blanket’ wrapped around Mars’ core. Their findings revealed new clues about the planet’s evolutionary history and the loss of its potential to sustain life.
- How To Preserve Beneficial Hibernating Insects in Your Yard – Raking and disposing of fallen leaves can disrupt a delicate ecosystem, according to research conducted by Entomology Ph.D. candidate Max Ferlauto.
- New Small Laser Device Can Help Detect Signs of Life on Other Planets – A UMD-led team developed a new instrument specifically tailored to the needs of NASA space missions. Their mini laser-sourced analyzer is significantly smaller and more resource-efficient than its predecessors—all without compromising the quality of its ability to analyze planetary material samples and potential biological activity onsite. The team’s paper on the new device was published in Nature Astronomy in January 2023.
Take a look at our top stories from previous years.